Dec 16, 2022
7 min to read
Selling on Amazon is a great way to reach new audiences and grow your revenue, but it’s not quite as simple as logging in and uploading your inventory. When it comes to selling your products on Amazon there are two different business models: Amazon Seller and Amazon Vendor.

It’s no secret that Amazon has dominated the eCommerce landscape for the past decade or so. Customers go there to find new products and to buy what they need. 74% of Amazon customers say they use Amazon to discover new brands and in the United States alone 7,400 products are purchased every minute. With two-day shipping, seamless returns, and tons of options, it’s easy to turn to marketplace giant for your shopping needs, and Amazon’s growth isn’t slowing down. It’s clear to see why brands and retailers need to take full advantage of this digital behemoth.
Selling on Amazon is a great way to reach new audiences and grow your revenue, but it’s not quite as simple as logging in and uploading your inventory. When it comes to selling your products on Amazon there are two different business models: Amazon Seller Central and Amazon Vendor Central. Let’s break them down and determine which combination might be the best for you.
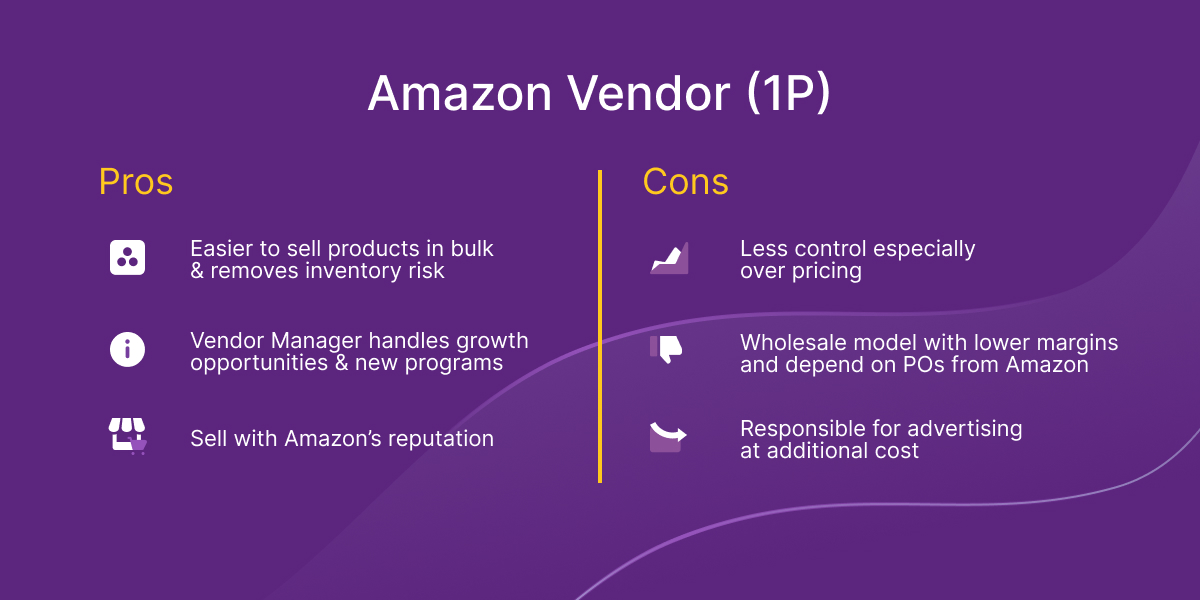
Being an Amazon Vendor essentially means that you are a wholesale supplier, selling your products to Amazon. This means that you receive a purchase order from Amazon, fulfill the purchase order, and sell your products directly to Amazon. In rare cases, direct fulfillment is an option even as a vendor, however it requires robust warehousing and fulfillment capabilities. It’s important to note that you must be invited by Amazon to be a Vendor.
Most often first-party vendors are brands that may sell D2C on other channels, but in this instance Amazon is now the retailer that is selling your product. This means that you set the list price, but the selling price is determined by the market. Each year when you negotiate your contract with Amazon you negotiate your margins directly.
Although Amazon is now the owner and seller of the products, you are still responsible for setting up the item and for providing some of the product content. Amazon will make some optimizations on the product detail page for you, but you must also make efforts to ensure that your product record is complete and accurate, to ensure that your products sell and Amazon wants to place more purchase orders with you. You also still have the ability to advertise and run promotions for your products so they sell faster and Amazon continues to buy more from you.
Vendor Central
First-party Amazon vendors manage their relationship with Amazon through Vendor Central. That’s where you can make updates to product listings, view purchase orders, and access available reporting.
What are the benefits of being a first-party Amazon vendor?
Selling as a first-party vendor on Amazon tends to be easier than third-party selling. This is because it works like a wholesaling model. By fulfilling Amazon’s purchase order, you can take advantage of a much more hands-off approach, while still taking advantage of the volume of consumers shopping on Amazon.
Furthermore, you can take advantage of the trust that comes with being an Amazon Vendor. This allows you to take advantage of Amazon’s reputation for fast shipping and easy returns. When potential customers see ‘Sold By Amazon’ you get the added value of perceived trust from consumers.
What are some of the downsides of being an Amazon Vendor?
When you sell your products directly to Amazon you no longer have control over your products. One aspect of that includes pricing. Since Amazon determines the price of your product depending on the market, and you are acting as a wholesale supplier for Amazon, you may have lower profit margins. Typically, on an annual basis, you negotiate your margins directly with Amazon. This can mean there is less predictability than a 3P Seller that pays a flat percentage fee.
While Amazon Vendors have access to more marketing and advertising options which can be a bonus, they are still responsible for any additional costs associated with them. For example, in order to move product quickly, an Amazon Vendor may wish to run Sponsored Product Advertisements on Amazon which they pay for on a cost-per-click basis. The Vendor is responsible for all fees and managing all campaigns to market and advertise the products.
When you’re a third-party Amazon Seller you use the Amazon marketplace as a channel to sell your products directly to consumers shopping on Amazon. You are responsible for the product listings, marketing and advertising, as well as the fulfillment of any orders. Amazon third-party sellers have access to different types of fulfillment options.
The fulfillment options for third-party sellers include: FBA (fulfilled by Amazon), FBM (fulfilled by merchant) and SFP (seller fulfilled prime).
FBA (Fulfilled by Amazon)
FBA is a shipment method where you as a seller send your inventory to different Amazon fulfillment centers. Amazon stores them in their warehouses, and when a customer orders it, they are responsible for shipping it and for the customer service. You, as the seller, pay a fee depending on the size and weight of the products.
FBM (Fulfilled by Merchant)
FBM is a method in which you as the seller are responsible for storing, shipping and all customer support when your product is purchased by a consumer on Amazon.
SFP (Seller Fulfilled Prime)
For some businesses with extensive shipping capabilities, enrolling in SFP is the best choice for fulfillment. This is a method where you commit to fulfilling orders that meet Prime qualifications of two-day delivery, at no additional cost to the customer, but do not utilize Amazon’s warehouses and shipping.
The majority of Amazon sellers, 92%, utilize FBA.
Seller Central
Third-party sellers on Amazon can access their seller accounts in a portal known as Seller Central.
What are the benefits of being an Amazon Seller?
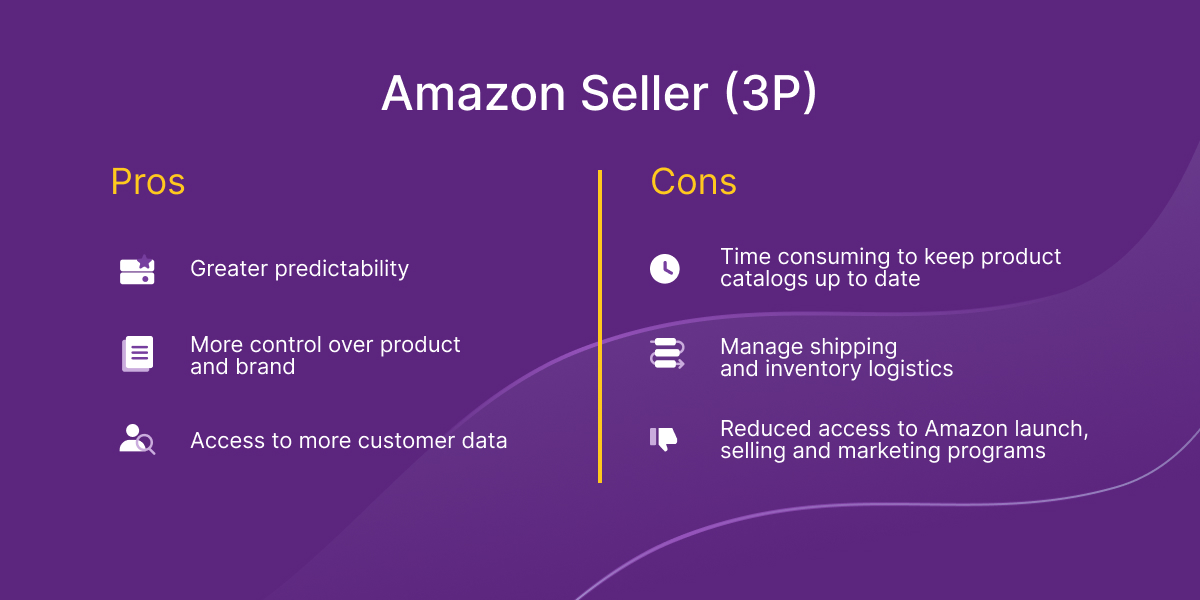
A major benefit of being an Amazon Seller is that you have more control over your prices. This means that you can maximize your margins on this channel. As an Amazon Seller you often pay a flat rate with fees. With this there can be more predictability for the costs, as opposed to Amazon Vendors that have contractual margins. Also, as a seller, you get more access to the information about the consumers that are buying your products.
What are the downsides of being an Amazon Seller?
Being an Amazon Seller means that you’re responsible for the product listing pages, product details, marketing, and more. That can often require a lot of time and effort to ensure that each listing is optimized. It’s challenging to manage large product catalogs.
Yes. Brands can utilize both business models when selling on Amazon, as they can serve different purposes.
Oftentimes a hybrid model is a great way to sell your products on Amazon. You can utilize Amazon Vendor to sell high volume items in your catalog with consistency, and take advantage of selling long-tail items or excess stock via the third-party model.
No matter your business model, selling on Amazon can help you reach your growth and revenue targets. With more and more consumers heading to Amazon to discover and purchase products every day, it’s more imperative than ever that you’re optimizing your customer’s experience on this massive eCommerce platform.
More than that, since consumers have so many options to choose from on Amazon, it’s important that you offer the best possible product experiences.
Akeneo can help you offer superior product experiences through Akeneo PIM, Akeneo Activation for Amazon Vendor, and other seamless connections wherever you sell your products. Reach out to an Akeneo expert today to learn more.
Sign up for our newsletter and stay ahead of the curve on everything you need to know about product information management, product experience management and how to unlock growth for your organization.
