Sustainability is transforming how brands and retailers operate. From resale and refurbishment to take-back programs, discover how businesses across fashion, food, electronics, and automotive industries are embracing the circular economy. Learn why accurate product information is the key to reducing waste, increasing customer trust, and making circular strategies a success.

Table of Contents
Keywords
We live in a time where customers view products as more than just items to purchase and gateways to the latest trend. More than ever, they’re looking at brands through a sustainability lens, and particularly within Gen Z: young consumers are 27% more likely to buy from businesses that are genuinely walking the sustainability talk.
In other words, being “green” isn’t just a nice bonus anymore - it can often be a dealbreaker for consumers, and brands and retailers have taken the hint. To meet these shifting expectations, many brands and retailers have embraced the circular economy not just as a sustainability flex, but as a real commitment to doing better. But what exactly is the circular economy, and how does it work in practice? Let’s find out!
Like its name suggests, the circular economy refers to a business model that aims to minimize waste by reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling products, materials, and resources. Unlike the traditional linear economy, the circular economy minimizes waste by keeping products and materials in use through resale and reuse. It’s about extending the life of products, components, and materials to reduce the environmental impact of production and consumption.
At its core, the circular economy flips the script on how we see products, materials, and consumption - turning “use and toss” into “use and reuse.” It's not just about buying and discarding; it’s about giving products a longer life, cutting down waste, and reimagining the retail landscape in a more eco-friendly way.
The circular economy isn’t a new idea, but it has taken center stage in recent years as environmental sustainability becomes increasingly urgent. Given its environmental impact, the need for this movement is greater than ever, offering benefits like less waste, lower use of finite resources, reduced carbon footprint, and significant cost savings. However, the benefits go beyond just the environment - they also offer significant advantages for businesses, such as:
Boosting in-store traffic: Implementing circular economy practices can increase store traffic by attracting eco-conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability in their shopping habits. Offering secondhand or refurbished products, repair services, and trade-in programs create new reasons for customers to visit their stores!
Building customer loyalty: Customer loyalty can be built by aligning with consumers’ growing demand for sustainability and ethical business practices. As shoppers become more environmentally conscious, they seek out brands that favour long-term value over short-term consumption. By offering services like those I mentioned above (including resale options and rental models), brands create an ongoing relationship with customers rather than a one-time transaction. These initiatives keep customers coming back, building trust and strengthening their connection to the brand.
Reducing returns: By focusing on durability and second-life programs, brands ensure customers get high-quality products that won’t end up back on the shelf due to defects or dissatisfaction. Plus, circular practices also encourage retailers to provide clearer product descriptions, sustainable packaging, and digital tools like augmented reality and virtual reality, helping shoppers make smarter choices upfront and keeping returns to a minimum.
Showcasing passion and commitment: Participating in the circular economy sends a strong message that your business cares about the environment by turning values into action. By implementing circular practices and having official certifications, companies can demonstrate that sustainability is not just a marketing message but a core part of their operations.
Creating upsell and cross-sell opportunities: When customers bring in products for resale or recycling, retailers have an opportunity to upsell new items or cross-sell related products, increasing revenue. For instance, repair services give brands and retailers the perfect chance to upsell customers to premium or upgraded versions when they bring in older items. Likewise, refurbished and secondhand goods open the door for cross-selling add-ons like accessories or warranties, turning sustainability into a smart strategy that benefits both businesses and consumers.
By practicing what they preach, businesses are finding innovative ways to extend product lifecycles and minimize waste. Here are some standout brands and retailers leading the charge in circularity!
Asket is a Swedish fashion brand known for their commitment to timeless clothing and radical transparency. Unlike fast fashion, Asket focuses on permanent collections rather than seasonal trends, minimizing waste and encouraging consumers to purchase high-quality, long-lasting clothing. And it doesn’t stop there. Through their repair and resale outlet, Asket ReStore, they refurbish and resell previously owned garments, keeping their clothing in circulation and out of landfills or incinerators.
Here’s how it works: Customers who want to return their pre-owned (and washed!) Asket garments can do so through the brand’s platform in exchange for store credit. The returned pieces are then inspected, cleaned, and refurbished before being resold at a lower price, ensuring they stay in circulation rather than being discarded. If items need minor repairs or alteration, Asket restores them to ensure they’re ready for a second life.
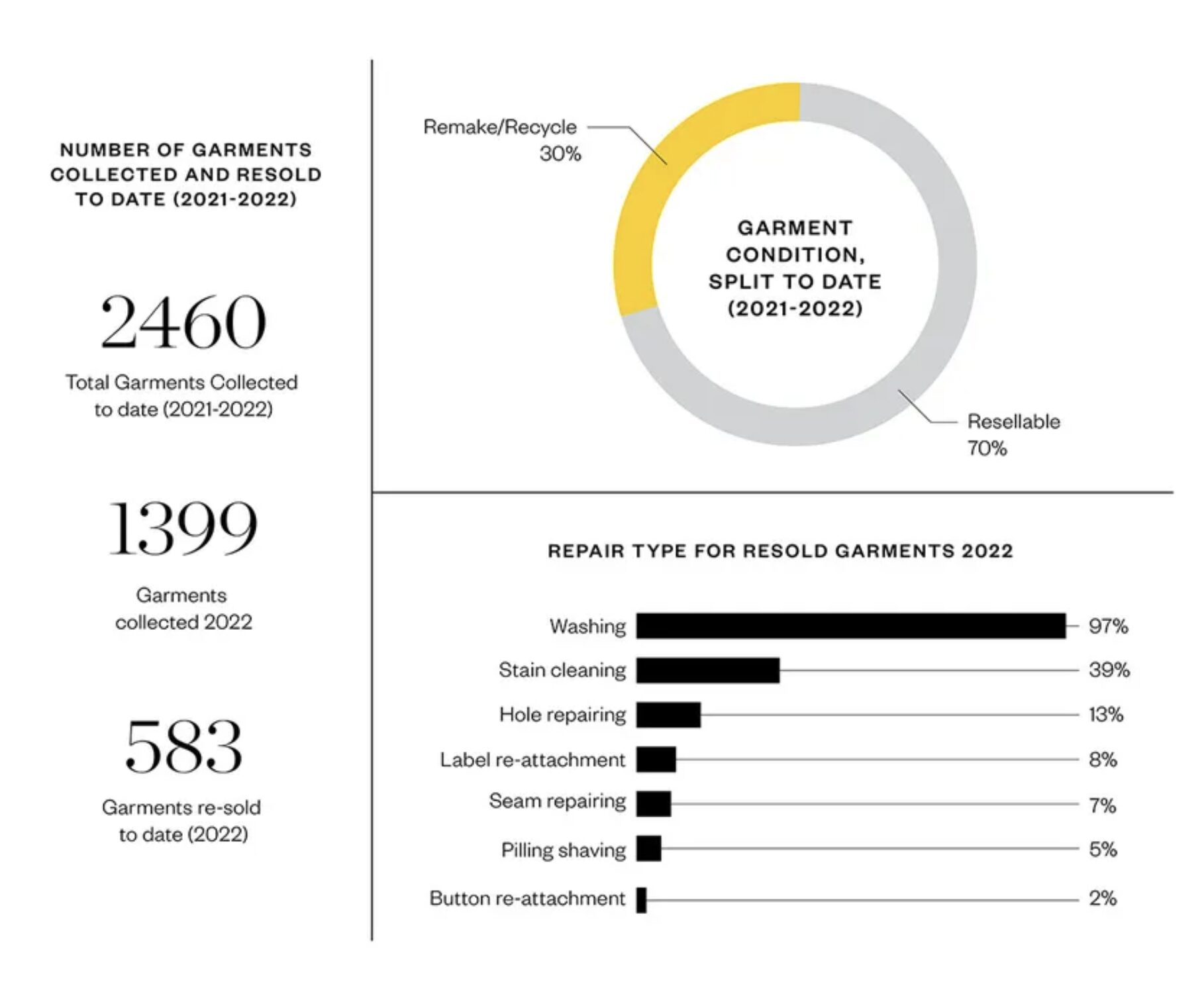
By offering secondhand options, Asket extends the lifespan of their products, proving that good style never goes out of fashion—nor does sustainability. Their initiative not only reduces textile waste but also provides customers with a more sustainable way to shop, making long-lasting clothing accessible while minimizing environmental impact.
To take things a stitch further, Asket partners with Fabrikörerna, a Swedish west coast organization that specializes in mending clothing and repurposing deadstock materials. Beyond textile revival, Fabrikörerna also serves as an integration project, helping immigrants learn Swedish and settle into their new communities. Through this partnership, Asket not only weaves together circular fashion but also supports social sustainability, proving that responsible business practices can make a meaningful impact beyond clothing!
The circular economy extends beyond traditional retail, and the mobile app, Olio, presents an innovative way to tackle food waste at the community level. Unlike platforms that focus on selling surplus food, Olio connects individuals, local businesses, and even supermarkets to share excess food for free. Whether it’s extra groceries, unopened pantry items, or fresh produce from a home garden, users can list and claim food that might otherwise go to waste, promoting a culture of sharing and sustainability.
For businesses, Olio makes food waste a thing of the past by offering an easy way to redistribute unsold food instead of throwing it away. Supermarkets (such as Tesco!), bakeries, and restaurants can donate excess stock, helping them cut waste disposal costs while contributing to local food security. By partnering with businesses and community volunteers, Olio ensures that perfectly good food finds plates, not landfills.

At an individual level, neighbors can use Olio to share food within their communities, making it easy to give away surplus items before they expire. Got extra home-cooked meals, too many groceries, or produce you won’t finish? Instead of letting it go to waste, simply list it on the app and let a neighbor pick it up. It’s like a digital “borrow a cup of sugar” moment—but for full meals! This simple list-and-pickup system makes sharing easy, reducing waste while building stronger community connections.
From an environmental standpoint, Olio plays a significant role in reducing food waste and lowering carbon emissions. By preventing food from being discarded, the app helps minimize methane emissions from decomposing food in landfills and conserves the resources used in food production, such as water, energy, and labor. With its community-driven approach, Olio turns waste reduction into a shared mission, making sustainable living not just possible, but deliciously easy!
When it comes to electronics, Back Market isn’t just a player—it’s a leader setting the standard for sustainable tech. They’re an online marketplace for refurbished electronics, making high-quality tech more affordable and sustainable by the minute. Founded in 2014 in France, the company challenges the idea that new is always better—offering refurbished smartphones, laptops, tablets, and more at up to 70% less than new. By working with professional refurbishers, Back Market ensures that customers receive thoroughly tested and certified products, often at significant discounts compared to brand-new devices.
At the heart of Back Market’s circular economy strategy is its trade-in program, which gives old electronics a second life while rewarding customers for making sustainable choices. What sets it apart from others is its convenience and transparency. Customers receive an instant price estimate for their device through the platform, and once the item is shipped and inspected by a professional refurbisher, the payment is processed quickly. Even devices that are no longer functional can still hold value, as they can be repaired, refurbished, or responsibly recycled. This ensures that every device gets a second chance, reducing e-waste and minimizing the need for new production.

(Source)
The platform not only helps extend the life of electronics but also reduces e-waste and the environmental impact of tech production. Manufacturing new devices requires vast amounts of raw materials, energy, and water, contributing to carbon emissions and resource depletion. By encouraging consumers to opt for refurbished products, Back Market helps curb this cycle.
Beyond just selling refurbished tech, Back Market is reshaping consumer perceptions of pre-owned electronics. Through a mix of witty marketing, transparency, and strict quality standards, the company has built a brand that makes sustainability cool and accessible. Their rigorous testing process, warranties, and customer satisfaction guarantees help build trust in the refurbished market, making it easier for people to switch to greener, more cost-effective tech choices. As demand for refurbished devices continues to grow, Back Market is proving that sustainability isn’t just a responsibility—it’s a thriving business opportunity!
Renault is driving the circular economy forward—literally. The company has embraced repair, reuse, and recycling to keep its vehicles and components on the road longer instead of sending them to the scrap heap. One of its most significant initiatives is the Refactory at Flins, the first European circular economy factory dedicated to mobility. This facility specializes in vehicle refurbishment, battery repair, parts remanufacturing, and materials recycling, ensuring that end-of-life vehicles and components are given a second life rather than being discarded. By implementing these processes, Renault not only minimizes waste but also reduces the need for new raw materials, aligning with the principles of the circular economy.
One of Renault’s most impactful circular initiatives is its battery refurbishment program—because why waste a perfectly good battery when you can give it a second life? Renault evaluates the health and capacity of used batteries, repairing or repurposing them for second-life applications, such as energy storage solutions. These refurbished batteries are then reintroduced into the market at a lower cost, making electric vehicle (EV) ownership more affordable while reducing the environmental impact of battery production. This initiative plays a crucial role in reducing raw material dependency and lowering carbon emissions associated with battery manufacturing.
It’s not just batteries getting a second chance—Renault is also reviving key vehicle components like engines, turbochargers, and gearboxes through its RE-FACTORY initiative. Instead of producing entirely new parts, the company repairs and reconditions used components, ensuring they meet original quality standards before reselling them. This lowers energy consumption, slashes material waste, and gives customers a more budget-friendly option—all while keeping perfectly good car parts from an early retirement.
By steering the auto industry toward circularity, Renault is proving that sustainability can drive side-by-side with vehicles. By extending the life of vehicles and components, reducing reliance on virgin materials, and implementing large-scale refurbishment programs, Renault is reshaping the industry’s approach to sustainability. These initiatives not only lessen the environmental footprint of car manufacturing but also offer economic benefits by creating more affordable, durable products for consumers. With innovation at the wheel, Renault is showing that the road to sustainability is one worth taking—and it’s got plenty of mileage left!
The circular economy thrives on transparency and accurate product data—all of which are made possible with a PIM (Product Information Management) system in your corner. For brands and retailers embracing circularity, a PIM ensures that key details like materials and durability are consistently communicated across all platforms. Whether it’s refurbished products, resale, or take-back programs, having a centralized system for managing product data makes it easier to keep items in circulation.
For brands and retailers, PIM is the secret tool that makes circularity work smoothly. With accurate product descriptions, sustainability certifications, and lifecycle details all in one place, businesses can cut returns, boost resale opportunities, and simplify refurbishment processes. Plus, with traceability and transparency at their fingertips, customers feel more confident choosing products that support sustainability. But PIM isn’t just about making circularity easier—it’s also about future-proofing businesses in a world where sustainability isn’t the status quo. As regulations tighten and consumer expectations shift, having a centralized, adaptable product data system ensures brands stay ahead of the curve.
In an era where sustainability is no longer optional, the circular economy presents a game-changing opportunity for brands and retailers. By embracing circular strategies, businesses can reduce waste, enhance customer loyalty, and contribute to a more sustainable future—all while strengthening their bottom line.
The key to making this shift successful? Accurate, transparent, and engaging product information. And this is effectively done when powered by a robust Product Information Management (PIM). The centralizing solution guarantees that no matter the channel, consumers have clear, consistent details about a product’s materials, durability, and end-of-life options—allowing them to make informed, eco-conscious choices. PIM streamlines sustainability efforts, making circular economy practices more accessible and effective for businesses.
The circular economy is the future of retail, and brands that embrace it stand to win big in both sustainability and customer loyalty. Because consumers are backing brands that walk the talk, and those embracing transparency and circularity won’t just save the planet—they’ll leave the competition in the dirt.
Discover how to avoid the pitfalls of greenwashing and build genuinely sustainable strategies that foster trust, align with regulations, and drive long-term business growth.
