Artificial intelligence is changing manufacturing by driving efficiency, improving product design, and streamlining supply chains. Learn how manufacturers can harness AI and product data management to innovate faster and deliver exceptional product experiences.

Table of Contents
Keywords
Manufacturing isn’t what it used to be. The factory floor has traded in clipboards and constant machine checks for smarter systems that never take a break.
In fact, 48% of manufacturers now use AI-driven predictive maintenance to stop breakdowns before they occur.
Artificial Intelligence has become a powerful engine for progress, taking over the repetitive tasks humans were never eager to do. While the more obvious applications of AI tend to be in the customer-facing areas like marketing and eCommerce, it can also work in the background to quietly keep production lines moving and the manufacturing industry evolving at full speed.
AI in manufacturing refers to the use of AI algorithms, machine learning, and other AI systems to support and enhance every stage of the manufacturing process. Unlike traditional automation, which follows rigid rules, AI can process large and complex streams of information, adapt in real time, and uncover insights that static systems miss.
At its core, AI in manufacturing is not about replacing the human element but about adding an intelligent layer to the systems already in place. AI models are built to recognize patterns and handle volumes of information far beyond the reach of traditional tools. The result is a manufacturing process that is more adaptive and resilient.
Unlike older systems bound by rigid instructions, AI introduces flexibility and continuous learning that gives manufacturers the ability to stay strong as customer expectations and technologies continue to advance.
AI is transforming efficiency in the manufacturing industry through predictive maintenance and automation that reduce downtime and streamline production lines. With predictive maintenance, AI algorithms track the health of machines in real time, detecting early warning signs of failure and allowing scheduled repairs before breakdowns occur.
A great example of this is Siemens MindSphere, an industrial IoT and AI-powered platform that connects factory equipment, collects sensor data, and predicts failures before they happen. By recommending optimal repair schedules and monitoring asset performance, MindSphere helps manufacturers avoid costly disruptions while maintaining peak efficiency.
Yet efficiency in manufacturing isn’t limited to machine health alone. AI systems also automate repetitive tasks that once consumed valuable human time, freeing workers to concentrate on more strategic responsibilities. From adjusting equipment settings on the fly to optimizing processes, AI applications ensure every stage of the manufacturing process runs at peak performance. The outcome is a faster operation that can adapt to changing demands without missing a beat!
AI-driven monitoring systems can oversee factory environments in real time, spotting hazards like overheating machinery, chemical leaks, or unsafe behaviors. By alerting teams early, these systems prevent accidents before they escalate, keeping people and operations out of harm’s way.
IBM Maximo Visual Inspection, an AI-powered tool within the IBM Maximo Application Suite (MAS), is a good example of these improved safety standards in practice. It uses computer vision to detect and identify unsafe conditions on the factory floor. Paired with predictive analysis, solutions like this give manufacturers early warnings, strengthen compliance with safety standards, and create safer working environments.
Beyond immediate detection, AI models process data from sensors and historical incidents to predict risks and enforce safety standards. Whether it’s forecasting equipment fatigue or identifying hazardous conditions, AI applications reinforce a culture of safety that reduces liability and creates a more resilient workplace for everyone.
Digital twin technology is the practice of creating a digital replica (or “twin”) of a physical asset, machine, or process. This virtual model is connected to real-world equipment through sensors and IoT devices, allowing it to mirror performance in real time. Because it continuously receives live data, the digital twin behaves just like the physical object it represents, making it a powerful tool for experimentation and insight.
With this approach, manufacturers can test scenarios and analyze data in a risk-free digital environment before applying changes to the real-world system. A factory could model how a new process would affect output or stress-test a machine virtually to uncover potential weaknesses in order to streamline the process and prevent costly mistakes that come with testing in live production.
Digital twins become even more powerful when paired with AI. While the twin provides the virtual model, AI algorithms predict outcomes and continuously refine simulations. This turns digital twins from static replicas into AI-driven systems that can optimize workflows and even suggest improvements for sustainability!
We can look to BMW’s iFactory strategy as an example of this concept in action, which uses digital twins enhanced with AI to design, test, and optimize production systems virtually before they’re rolled out on the shop floor. By creating a complete digital mirror of its factories, BMW can fine-tune workflows and ensure sustainability goals are met, all without disrupting real-world production.
When it comes to design, AI adds both intelligence and creativity to the process! AI systems sift through vast datasets (such as customer preferences and market trends) to suggest improvements for product designs. Instead of relying solely on intuition, engineers gain data-driven insights that accelerate innovation and reduce the risks of trial-and-error development.
A strong example of this in the manufacturing industry is Autodesk Generative Design, which uses AI algorithms to explore countless design possibilities based on performance goals and constraints, which enables manufacturers to quickly identify optimized designs that are stronger while using less material.
Beyond optimization, AI also speeds up the entire design process by transforming raw ideas into viable prototypes at record speed and enhancing functionality while leaving less room for waste! Ultimately, AI-driven design enhances human creativity and streamlines the process of transforming concepts into solutions that are ready for production more efficiently than ever.
The supply chain is one of the most complex aspects of the manufacturing industry, and AI is proving invaluable in making it more predictable and resilient. AI solutions powered by machine learning help manufacturers forecast demand with greater accuracy, allowing them to optimize inventory levels and avoid both shortages and overstock.
Beyond efficiency, AI introduces a new level of transparency. Manufacturers can now monitor every stage of the manufacturing process, ensuring compliance while identifying and addressing bottlenecks in real time. This is especially crucial as Digital Product Passport (DPP) legislation goes into effect in 2026 and requires an unprecedented level of supply chain transparency and collaboration.
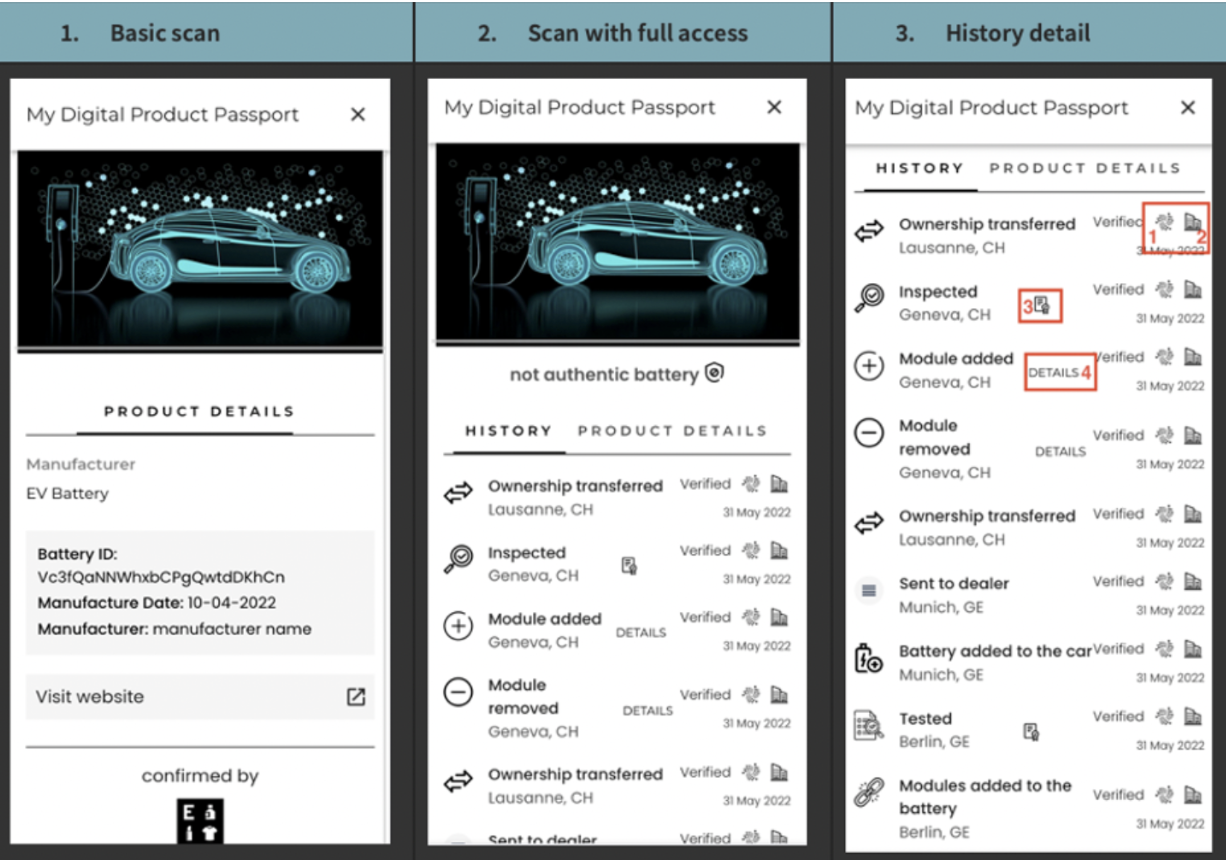
A solution like Akeneo’s Supplier Data Manager (SDM) can be very helpful when it comes to collecting and optimizing product data collected throughout the supply chain. SDM replaces outdated, manual processes with AI-driven automation that streamlines supplier data exchange and enrichment processes. By using shared templates and flexible workflows, suppliers can onboard product data at scale while manufacturers are able to ensure accuracy and consistency before bringing the data into Akeneo PIM.
Quality control is one of the areas where AI is making the most immediate impact. Traditional inspection methods often rely on human oversight and manual checks, which can miss subtle flaws.
A great example here is LandingLens by Landing AI, which is a tool that uses computer vision to inspect products in real time and catch defects that might otherwise go unnoticed. By reducing recalls and improving consistency, tools like this help manufacturers deliver excellent products at scale and ensure their quality is reliable at every stage of the manufacturing process.
With nearly half of all consumers willing to pay 25% more if a company were to clearly communicate sustainability practices, it’s no wonder that more and more manufacturers and merchants are looking to collect, track, and communicate this information.
From reducing material waste to lowering energy consumption, AI-driven systems improve production schedules and resource use in ways that lessen environmental impact without sacrificing performance. A strong example is Microsoft AI for Sustainability, which provides real-time insights into energy use and emissions, enabling manufacturers to track their footprint and take action.
The benefits go beyond compliance. AI enables manufacturing processes that are both efficient and responsible, reducing costs while aligning with regulations and consumer expectations for greener practices. Embedding AI into daily operations allows manufacturers to position themselves as both innovative and responsible, proving that progress and sustainability can go hand in hand.
From predictive maintenance and digital twins to supply chain resilience, AI is reshaping every corner of the manufacturing process. And with platforms like SDM, manufacturers can extend that intelligence beyond the factory floor into their product data, ensuring efficiency and accuracy.
The future of manufacturing lies in the hands of companies that embrace AI as a strategic partner. Those who invest today will be best positioned to deliver consistent product experiences and lead confidently into the next era of commerce.
Discover how AI is transforming shopping, search, and product experiences, and why clean, structured data is the key to staying competitive in the next era of commerce.
